이번 수업시간에는 Mybatis에서 트랜잭션을 다루는 방법을 배웠다. 특히 기존 클래스의 코드를 손대지 않고 일부 기능을 변경하는 프록시 디자인 패턴을 적용하였다.
실습
mini-pms-41-c-client
1단계: 트랜잭션을 다루기 전에 프로젝트 상세 조회 기능을 변경한다.
com.ecoms.pms.handler.ProjectDetailCommand
프로젝트 정보 외에 작업 목록을 추가로 출력한다.
TaskDao 인터페이스 변경: findAll(Msp<String, Object) 메서드를 변경한다.
1
List<Task> findByProjectNo(int projectNo) throws Exception;
실무에서는 인터페이스를 거의 변경하지 않는다. 그러면 인터페이스와 관련된 메서드를 모두 뜯어고쳐야 하고, 그러다 보면 돌아가던 코드도 돌아가지 않을 수 있다. 따라서 어쩔 수 없이 중복 코드를 계속 붙여나가는 방법을 사용한다.
TaskDaoImpl 클래스 변경: findAll(Msp<String, Object) 메서드를 변경한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
@Override
public List<Task> findByProjectNo(int projectNo) throws Exception {
try (SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession()) {
return sqlSession.selectList("TaskDao.findByProjectNo", projectNo);
}
}
TaskListCommand 변경: findAll(null) 호출 코드를 변경한다.
1
List<Task> list = taskDao.findAll(null);
TaskMapper.xml 변경: findAll SQL을 변경한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
<select id="findAll" resultMap="TaskMap" parameterType="map">
select
t.no,
t.content,
t.deadline,
t.status,
m.no owner_no,
m.name owner_name
from
pms_task t
inner join pms_member m on t.owner=m.no
<where>
<if test="projectNo != null">
t.project_no = #{projectNo}
</if>
</where>
order by t.deadline asc
</select>
ProjectDetailCommand 변경: 프로젝트 정보 외에 작업 목록을 추가로 출력한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
public class ProjectDetailCommand implements Command {
ProjectDao projectDao;
TaskDao taskDao;
public ProjectDetailCommand(ProjectDao projectDao, TaskDao taskDao) {
this.projectDao = projectDao;
this.taskDao = taskDao;
}
@Override
public void execute(Map<String,Object> context) {
System.out.println("[프로젝트 상세보기]");
int no = Prompt.inputInt("번호? ");
try {
Project project = projectDao.findByNo(no);
if (project == null) {
System.out.println("해당 번호의 프로젝트가 존재하지 않습니다.");
return;
}
System.out.printf("프로젝트명: %s\n", project.getTitle());
System.out.printf("내용: %s\n", project.getContent());
System.out.printf("기간: %s ~ %s\n",
project.getStartDate(),
project.getEndDate());
System.out.printf("관리자: %s\n", project.getOwner().getName());
System.out.print("팀원: ");
project.getMembers().forEach(
member -> System.out.print(member.getName() + " "));
System.out.println();
System.out.println("작업: ");
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("projectNo", project.getNo());
List<Task> tasks = taskDao.findAll(map);
System.out.println("번호, 작업내용, 마감일, 작업자, 상태");
for (Task task : tasks) {
String stateLabel = null;
switch (task.getStatus()) {
case 1:
stateLabel = "진행중";
break;
case 2:
stateLabel = "완료";
break;
default:
stateLabel = "신규";
}
System.out.printf("%d, %s, %s, %s, %s\n",
task.getNo(),
task.getContent(),
task.getDeadline(),
task.getOwner().getName(),
stateLabel);
}
System.out.println();
2단계: 현재 프로젝트에서 트랜잭션을 다루는 방식과 문제점을 이해한다.
ProjectDeleteCommand
ProjectDeleteCommand가 TaskDao의 deleteByProjectNo() 메서드를 호출한다. 객체지향 언어로는 메시지를 보낸다고 한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
public class ProjectDeleteCommand implements Command {
//...
@Override
public void execute(Map<String,Object> context) {
//..
try {
// 프로젝트에 소속된 모든 작업 삭제하기
taskDao.deleteByProjectNo(no);
// 프로젝트 삭제하기
if (projectDao.delete(no) == 0) {
System.out.println("해당 번호의 프로젝트가 존재하지 않습니다.");
return;
ProjectDao
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
public class ProjectDaoImpl implements com.eomcs.pms.dao.ProjectDao {
//..
@Override
public int delete(int no) throws Exception {
try (SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession()) {
// 프로젝트에 소속된 모든 멤버를 삭제한다.
sqlSession.delete("ProjectDao.deleteMembers", no);
// => 프로젝트를 삭제한다.
int count = sqlSession.delete("ProjectDao.delete", no);
sqlSession.commit();
return count;
}
}
TaskDao
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
public class TaskDaoImpl implements com.eomcs.pms.dao.TaskDao {
//...
@Override
public int deleteByProjectNo(int projectNo) throws Exception {
try (SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true)) {
return sqlSession.delete("TaskDao.deleteByProjectNo", projectNo);
}
}
즉 그림으로 나타내면 다음과 같다.
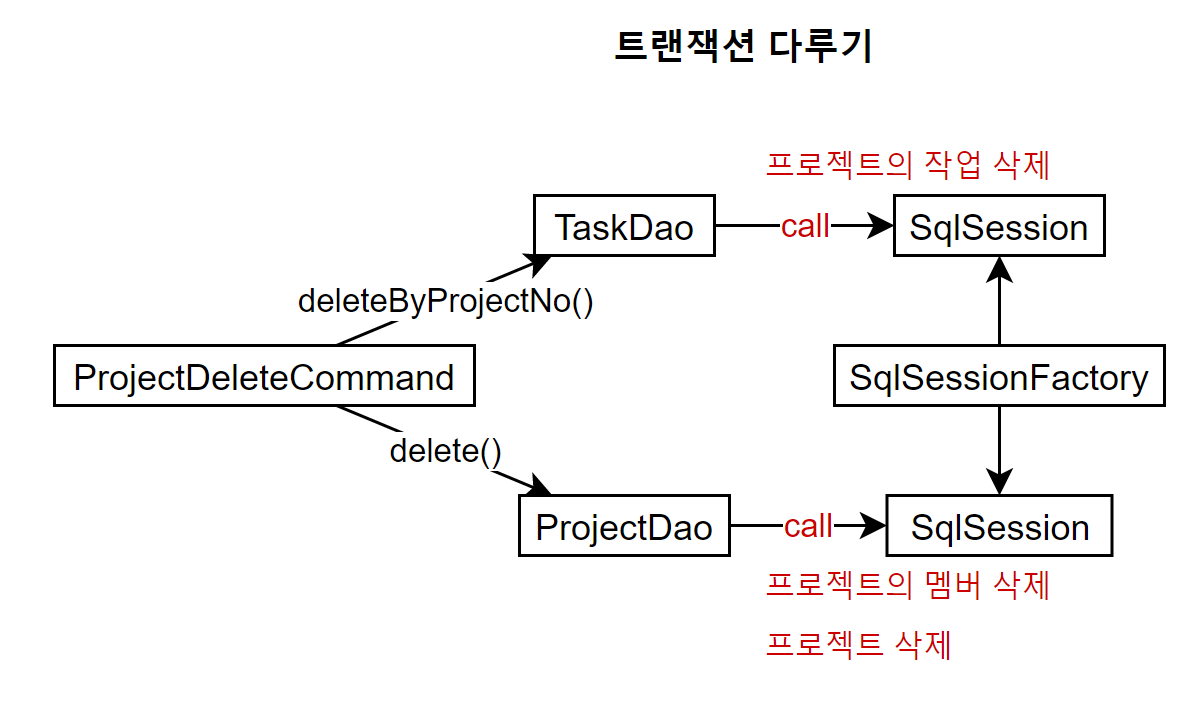
ProjectDeleteCommand는 우선 TaskDao를 통해 작업을 삭제하고, ProjectDao를 통해 프로젝트 멤버와 프로젝트를 삭제한다. mybatis에서 트랜잭션은 SqlSession 단위로 관리한다. 그런데 현재는 작업을 삭제할 때의 SqlSession과 프로젝트 멤버 삭제와 프로젝트 삭제할 때의 SqlSession이 별개의 Sql 세션이다. 다시 말해, 프로젝트 멤버 삭제와 프로젝트 삭제 작업은 한 트랜젝션으로 묶여 있으나, 작업 삭제는 다른 트랜잭션에서 수행한다. 따라서 프로젝트 삭제 중에 예외가 발생한다면, 프로젝트 멤버 삭제는 자동 취소되지만, 같은 트랜잭션에 묶여 있지 않은 작업 삭제는 취소되지 않는다.
트랜잭션: 데이터 베이스의 상태를 변환시키는 하나의 논리적 기능을 수행하기 위한 작업의 단위 또는 한꺼번에 모두 수행되어야 할 일련의 연산들을 의미한다.
이를 확인하기 위해 프로젝트 멤버 삭제 후 일부러 예외를 발생시켜 보았다. 프로젝트 멤버 삭제는 취소되었으나 작업삭제는 취소되지 않았다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
@Override
public int delete(int no) throws Exception {
try (SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession()) {
// 프로젝트에 소속된 모든 멤버를 삭제한다.
sqlSession.delete("ProjectDao.deleteMembers", no);
// 프로젝트 멤버 삭제 후 예외를 발생시킨다.
if (100 == 100) {
throw new Exception("일부러 예외 발생!");
}
// => 프로젝트를 삭제한다.
int count = sqlSession.delete("ProjectDao.delete", no);
sqlSession.commit();
return count;
}
}
컴파일러는 소스코드에 문제가 있는지 아닌지만 확인한다. 따라서 그냥
throw new Exception()했을 때는 컴파일 자체가 안되지만 무조건 참인if(100==100)조건 실행 시throw new Exception()을 실행하도록 만들었을 때는 컴파일이 된다. 컴파일러는 실행하지 않고 문법적으로만 확인하기 때문이다.
TaskDaoImppl.deleteByProjectNo()에서 사용한 SqlSession 객체와 ProjectDaoImpl.delete()에서 사용한 SqlSession 객체가 다르기 때문이다. Mybatis에서는 각 SqlSession이 트랜잭션을 관리한다.
DAO 객체에서 트랜잭션을 다루는 안 되는 이유는 무엇일까? DAO의 각 메서드는 작업을 수행하기 위해 현재 별도의 SqlSession 객체를 사용한다. 트랜잭션은 SqlSession 객체에서 제어한다. 즉 DAO 각 메서드마다 트랜잭션이 분리되어 있다. 실습 상황처럼 DAO 각 메서드마다 트랜잭션이 분리되어 있으면 여러 DAO의 메서드를 묶어서 한 단위로 작업할 때 통제할 수 없는 문제가 발생한다.
해결책은 DAO의 각 메서드가 트랜잭션을 통제하지 않도록 한다. 그럼 누가 트랜잭션을 통제하는가? DAO를 사용하는 Command 객체가 통제하게 한다. 즉 트랜잭션 통제권을 DAO를 사용하는 객체로 넘긴다.
3단계: Command 객체에서 트랜잭션을 통제
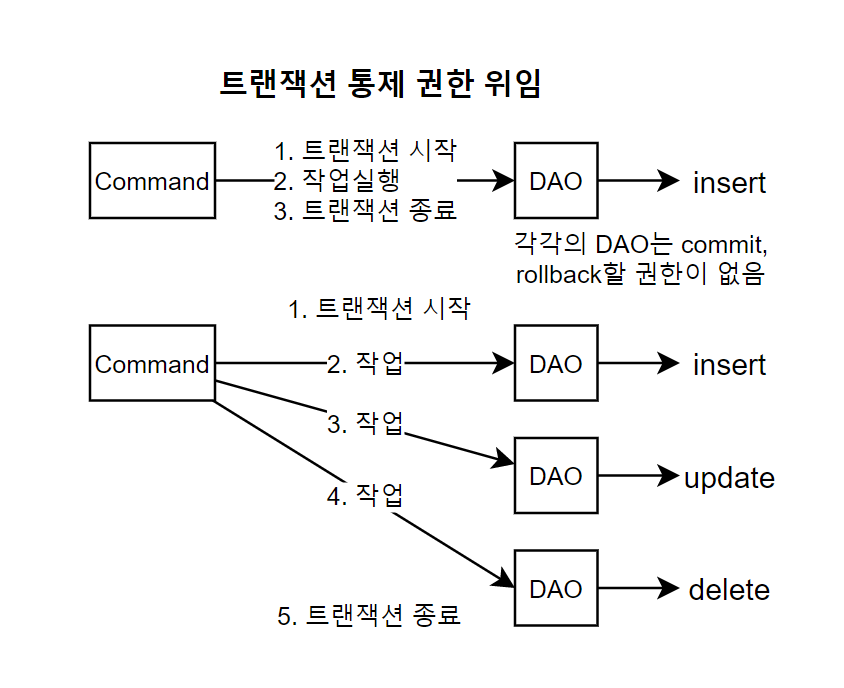
서로 다른 SqlSession 객체의 작업을 한 트랜잭션으로 묶어보자.

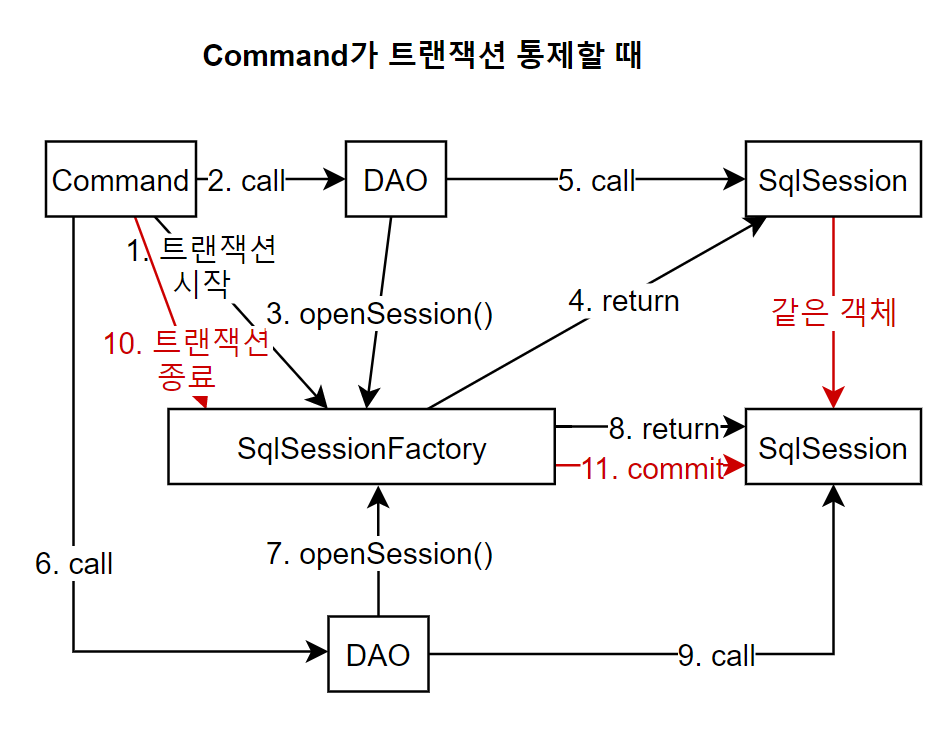
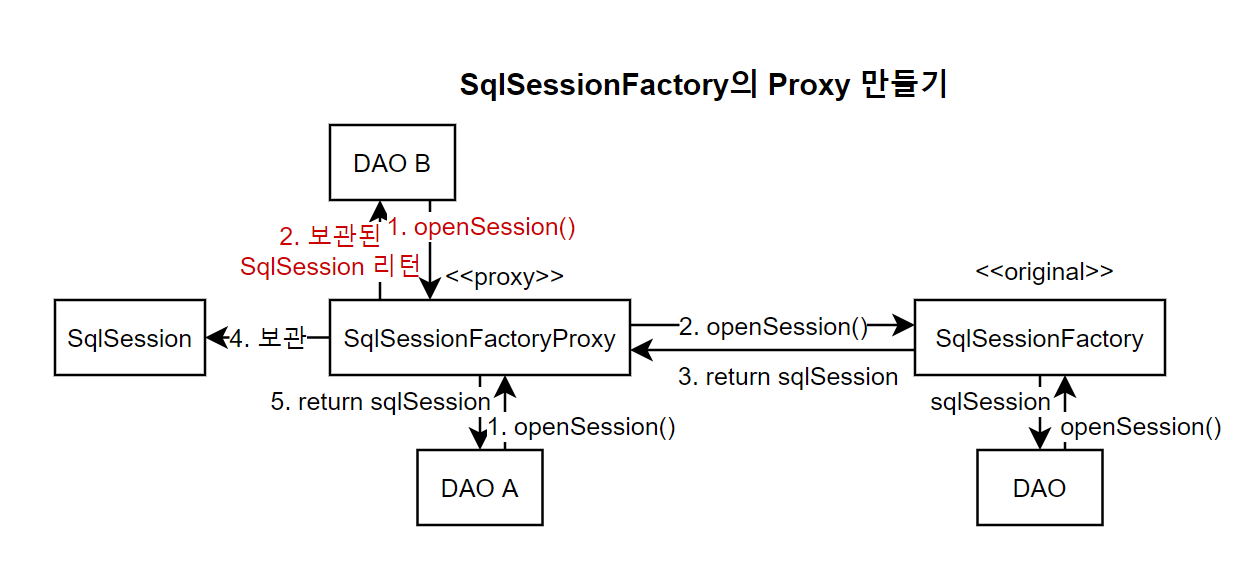
Command가 SqlSessionFactory에게 트랜잭션을 시작하라고 메시지를 보내고, DAO의 메서드를 호출한다. 그러면 DAO는 SqlSessionFactory의 openSession()을 호출하고 SqlSession 객체를 리턴받는다. 그리고 DAO는 SqlSession 객체를 사용하여 작업을 처리한다. 그리고 Command는 또 다른 DAO를 호출한다. 그러면 DAO가 SqlSessionFactory를 호출한다. 이때 SqlSessionFactory에게 Session 객체를 요청하면 (openSession()) SqlSessionFactory는 트랜잭션이 아직 종료되지 않았음을 확인하고 아까와 같은 SqlSession 객체를 리턴한다. 그럼 DAO는 이 객체를 통해 작업을 처리한다. 그런 후 Command는 트랜잭션 종료를 SqlSessionFactory에게 알린다. 그럼 팩토리 객체는 SqlSession의 commit() 메서드를 호출하여 테이블에 이때까지 한 작업을 반영한다. 이러한 과정을 통해서 각기 다른 DAO에서 한 작업을 하나의 트랜잭션으로 묶을 수 있다. 그러나 이러한 과정은 현재 구조에서 불가능하다. 다만 Proxy 패턴을 이용하여 이를 적용할 수 있다.
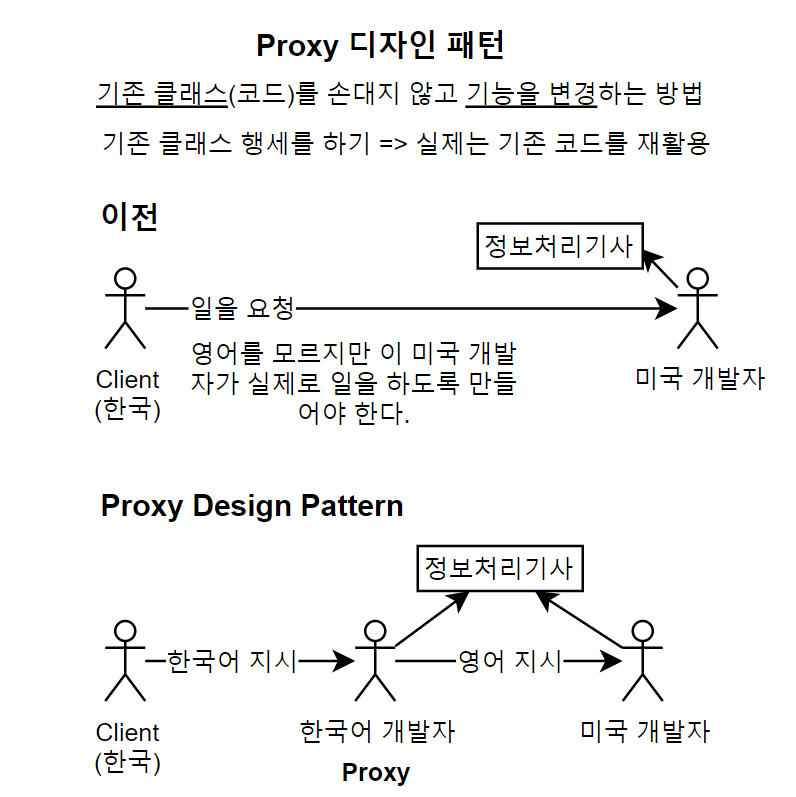
DAO가 아니라 Command가 트랜잭션을 통제하도록 만들기 위해서는 프록시 디자인 패턴을 적용해야 한다. 만약 정보처리기사를 가진 미국 개발자에게 일을 시켜야 한다고 하자. 그러나 이 클라이언트는 영어를 모르고, 미국 개발자는 한국어를 모른다. 그러면 어떻게 해야 할까? 한 가지 방법은 영어를 할 줄 알고, 정보처리기사 자격증을 가진 한국인 대리인을 세우고 대리인에게 한국어로 지시한 후 이 한국인 개발자가 미국 개발자에게 그대로 영어로 지시를 하도록 만드는 것이다. 이처럼 기존 클래스(미국 개발자) 행세를 하는 대리인을 내세워 기능을 변경하도록 만드는 것을 프록시 패턴이라고 한다.
com.eomcs.util.SqlSessionFactoryProxy 클래스 생성
Mybatis의 SqlSessionFactory 구현체의 대리 역할을 수행할 클래스를 정의한다. 이런 객체를 프록시(proxy)라고 부른다. 프록시는 반드시 원래 객체와 같은 인터페이스를 구현해야 한다.
두 메서드가 별개의 SqlSession 객체를 사용하기 때문에 문제가 발생하였다. 따라서 같은 SqlSession을 사용하도록 만들어야 한다. Mybatis를 통제하기 위해서는 SqlSession을 통제해야 한다. SqlSession이 달라버리면 commit, rollback을 함께 할 수 없다. 이때 SqlSession을 만드는 객체가 SqlSessionFactory이다. 따라서 SqlSession 대리 역할을 수행하는 클래스를 정의하면 된다. 마치 자신이 SqlSessionFactory인 것처럼 행동한다. 다른 메서드는 거의 비슷하지만 (기존 SqlSessionFactory의 메서드를 그대로 호출) 특정 메서드(
openSession())를 오버라이딩하고 특정 메서드(comit(),rollback()를 추가한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
public class SqlSessionFactoryProxy implements SqlSessionFactory {
SqlSessionFactory original;
public SqlSessionFactoryProxy(SqlSessionFactory original) {
// 생성자에서 원래의 구현체를 받아 보관해둔다.
this.original = original;
}
Source > generate delegate original의 메서드를 호출하도록 만든다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
public SqlSession openSession() {
return original.openSession();
}
public SqlSession openSession(boolean autoCommit) {
return original.openSession(autoCommit);
}
public SqlSession openSession(Connection connection) {
return original.openSession(connection);
}
public SqlSession openSession(TransactionIsolationLevel level) {
return original.openSession(level);
}
public SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType) {
return original.openSession(execType);
}
public SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType, boolean autoCommit) {
return original.openSession(execType, autoCommit);
}
public SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level) {
return original.openSession(execType, level);
}
public SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType, Connection connection) {
return original.openSession(execType, connection);
}
public Configuration getConfiguration() {
return original.getConfiguration();
}
기존 클래스에 없는 메서드를 추가한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
public class SqlSessionFactoryProxy implements SqlSessionFactory {
SqlSessionFactory original;
boolean inTransaction = false;
SqlSession currentSqlSession;
public SqlSessionFactoryProxy(SqlSessionFactory original) {
// 생성자에서 원래의 구현체를 받아 보관해둔다.
this.original = original;
}
// 기존 클래스에 없는 메서드를 추가한다.
public void startTransaction() {
inTransaction = true;
}
SqlSessionFactoryProxy.opensession()
이때 openSession() 메서드를 오버라이드한다. 트랜잭션이 시작 중일 때는 수동 커밋 상태의 SqlSession을 만들고, 나중에 다시 쓸 수 있도록 보관한 후 리턴한다. 만약 트랜잭션이 시작 중일 때 currentSqlSession이 존재한다면 기존 currentSqlSession을 리턴한다. 같은 SqlSession을 리턴해야 여러 작업을 한 트랜잭션으로 묶을 수 있기 때문이다. 트랜잭션이 시작 중이 아닐 때는 자동 커밋 상태의 SqlSession을 리턴하고, 따로 보관해두지는 않는다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
public SqlSession openSession() {
if (inTransaction) {
if (currentSqlSession == null) {
// 트랜잭션이 시작 중일 때는 수동 커밋 상태의 SqlSession을 만든다.
// 나중에 다시 쓸 수 있도록 보관해둔다.
currentSqlSession = original.openSession();
return currentSqlSession;
}
// 기존에 만든 SqlSession을 리턴해준다.
// 왜? 같은 SqlSession을 리턴해줘야 여러 작업을 한 트랜잭션으로 묶을 수 있다.
return currentSqlSession;
}
// 트랜잭션이 시작 중이 아닐 때는 자동 커밋 상태의 SqlSession을 리턴한다.
// 따로 보관해두지 않는다.
return original.openSession(true);
}
SqlSessionFactory.commit()
만약 currentSqlSession이 있다면 같은 SqlSession을 사용하여 수행한 모든 작업을 commit한다. 트랜잭션 작업을 종료한 후에는 SqlSession 객체를 제거한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
public void commit() {
// 같은 SqlSession을 사용하여 수행한 모든 작업을 commit한다.
if (currentSqlSession != null) {
inTransaction = false;
currentSqlSession.commit();
currentSqlSession = null;
// 트랜잭션 작업을 종료한 후에는 SqlSession 객체를 제거한다.
}
}
SqlSessionFactory.rollback()
만약 currentSqlSession이 있다면 같은 SqlSession을 사용하여 수행한 모든 작업을 rollback한다. 트랜잭션 작업을 종료한 후에는 SqlSession 객체를 제거한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
public void rollback() {
// 같은 SqlSession을 사용하여 수행한 모든 작업을 rollback한다.
if (currentSqlSession != null) {
inTransaction = false;
currentSqlSession.rollback();
currentSqlSession = null;
// 트랜잭션 작업을 종료한 후에는 SqlSession 객체를 제거한다.
}
}
mybatis는 SqlSession 단위로 작업을 한다. 따라서 한 작업은 같은 SqlSession으로 묶어야 한다. 이제 SqlSession 객체를 주는 것은 따로 정의한 SqlSessionFactoryProxy에서 하기 때문에 신경 안쓰고 SqlSession 객체만 받아서 작업을 하면 된다.
AppInitListener
1
2
3
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryProxy(
new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(
Resources.getResourceAsStream("com/eomcs/pms/conf/mybatis-config.xml")));
기존 DAO는 original을 사용하는 것이 아니라 Proxy를 사용한다.
여러 작업을 트랜잭션으로 묶어서 다룰 경우 트랜잭션 제어는 Command 객체에서 한다.
TaskDaoImpl.deleteByProjectNo()
deleteByProjectNo() 메서드에서 SqlSession을 얻을 때 수동 커밋 상태에 SqlSession을 사용하도록 변경한다. 다른 작업과 묶을 수 있도록 하기 위함이다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
@Override
public int deleteByProjectNo(int projectNo) throws Exception {
try (SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession()) {
return sqlSession.delete("TaskDao.deleteByProjectNo", projectNo);
}
}
ProjectDaoImpl.delete()
delete()에서 트랜잭션을 제어하는 코드를 없앤다. 트랜잭션 제어는 DAO를 사용하는 측에서 해야 하기 때문이다. 상황에 따라 여러 개의 DAO에서 수행한 작업을 한 트랜잭션을 묶어서 다룰 경우가 있다. 이런 상황에서 각각의 DAO가 트랜젝션을 제어해서는 안된다.각각의 DAO가 commit(), rollback()을 하게 되면 트랜잭션 제어가 안 되기 때문이다
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
@Override
public int delete(int no) throws Exception {
try (SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession()) {
// 프로젝트에 소속된 모든 멤버를 삭제한다.
sqlSession.delete("ProjectDao.deleteMembers", no);
// 프로젝트 멤버 삭제 후 예외를 발생시킨다.
if (100 == 100) {
throw new Exception("일부러 예외 발생!");
}
// => 프로젝트를 삭제한다.
int count = sqlSession.delete("ProjectDao.delete", no);
//sqlSession.commit();
return count;
}
}
실무에서는 DAO 안에서 트랜잭션 제어를 하면 안 된다. 절대 commit(), rollback()이나 자동 커밋을 설정해서는 안된다!
com.eomcs.pms.handler.ProjectDeleteCommand 클래스 변경: 여러 작업을 트랜잭션을 묶어서 다룰 경우 트랜잭션 제어는 Command 객체에서 한다.
예외 없이 실행이 정상적으로 완료되었다면, sqlSessionFactoryProxy에게 commit 요청한다. SqlSessionFac
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
public class ProjectDeleteCommand implements Command {
ProjectDao projectDao;
TaskDao taskDao;
SqlSessionFactoryProxy factoryProxy;
public ProjectDeleteCommand(ProjectDao projectDao, TaskDao taskDao, SqlSessionFactoryProxy factoryProxy) {
this.projectDao = projectDao;
this.taskDao = taskDao;
this.factoryProxy = factoryProxy;
}
//..
try {
factoryProxy.startTransaction();
// 프로젝트에 소속된 모든 작업 삭제하기
taskDao.deleteByProjectNo(no);
// 프로젝트 삭제하기
if (projectDao.delete(no) == 0) {
System.out.println("해당 번호의 프로젝트가 존재하지 않습니다.");
//factoryProxy.rollback(); => 할 필요가 없다!
return;
}
System.out.println("프로젝트를 삭제하였습니다.");
factoryProxy.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
factoryProxy.rollback();
System.out.println("프로젝트 삭제 중 오류 발생!");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
SqlSession.endTransaction()
트랜잭션이 성공하든 실패하든 종료될 때는 반드시 트랜잭션 상태를 초기화시킨다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
public void endTransaction() {
inTransaction = false;
// 이전에 commit()/rollback()을 호출하여 트랜잭션을 종료한 상태라면
// 다음 작업을 수행할 필요가 없다.
if (currentSqlSession != null) {
// 트랜잭션을 종료할 때 진짜 SqlSession 객체를 닫는다.
currentSqlSession.realClose();
}
currentSqlSession = null;
// 트랜잭션을 종료할 때 진짜 SqlSession 객체를 닫는다.
}
//..
public void commit() {
// 같은 SqlSession을 사용하여 수행한 모든 작업을 commit한다.
if (currentSqlSession != null) {
inTransaction = false;
}
endTransaction();
}
public void rollback() {
// 같은 SqlSession을 사용하여 수행한 모든 작업을 rollback한다.
if (currentSqlSession != null) {
currentSqlSession.rollback();
}
endTransaction();
}
ProjectDeleteCommand
성공하든 실패하든 endTransaction을 호출한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
System.out.println("프로젝트를 삭제하였습니다.");
factoryProxy.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
factoryProxy.rollback();
System.out.println("프로젝트 삭제 중 오류 발생!");
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
factoryProxy.endTransaction();
}
}
여러 개의 DAO 작업을 한 트랜잭션으로 만들기 위해서 위와 같이 코드를 변경하였다. 트랜잭션 처리는 DAO를 사용하는 쪽에서 하도록 한다.
원본 클래스를 바꾸지 않고 기능을 바꾸는 방법은 똑같이 인터페이스를 구현한 클래스를 만들고, 오리지널 객체를 가지고 있다가 일을 시키도록 한다. 다만 필요하면 메서드를 추가하거나 변경한다(openSession()) 원본 클래스에 인터페이스가 없다면? 똑같은 수퍼클래스를 상속받는다. 수퍼클래스가 없다면? 해당 객체를 상속받는다. 그러나 보통 인터페이스가 있다.
프로젝트를 삭제하려고 할 때 다음과 같은 예외가 발생하였다.
1
### Error updating database. Cause: org.apache.ibatis.executor.ExecutorException: Executor was closed.
왜 이런 예외가 발생할까? 실행자가 닫혀있기 때문이다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
@Override
public int deleteByProjectNo(int projectNo) throws Exception {
try (SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession()) {
return sqlSession.delete("TaskDao.deleteByProjectNo", projectNo);
}
}
try~resources 문법을 메서드 호출이 끝나면 sqlSession 객체를 닫도록 만들었기 때문이다. 하지만 자원은 항상 닫아줘야 한다. 그럼 어떻게 해야 할까?SqlSessionFactoryProxy에서 close()를 바꿔야 한다.
SqlSessionProxy 클래스 생성
Mybatis의 SqlSession 구현체의 대리 역할을 수행할 클래스를 정의한다. SqlSessionProxy 클래스를 생성한다. close() 메서드를 재정의한다. 트랜잭션을 수행 중인 상태에서는 close()가 동작되지 않도록 막는다.
SqlSessionFactoryProxy가 사용할 realClose()를 따로 만든다. 이 메서드는 원래 객체에 대해 close()를 실행한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
public void realClose() {
original.close();
}
@Override
public void close() {
//기능을 막아버린다.
}
즉 sqlSessionProxy를 가지고 close()를 아무리 호출해도 오리지널에게 전달을 하지 않는다. 단 realClose()를 호출하면 그때서야 오리지널에게 전달한다(닫으라고 명령한다).
이제 SqlSessionFactoryProxy에서 SqlSessionProxy를 사용한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
public class SqlSessionFactoryProxy implements SqlSessionFactory {
SqlSessionFactory original;
boolean inTransaction = false;
SqlSessionProxy currentSqlSession;
public SqlSessionFactoryProxy(SqlSessionFactory original) {
// 생성자에서 원래의 구현체를 받아 보관해둔다.
this.original = original;
}
// 기존 클래스에 없는 메서드를 추가한다.
public void startTransaction() {
inTransaction = true;
}
public void endTransaction() {
inTransaction = false;
// 트랜잭션 작업을 종료한 후에는 SqlSession 객체를 제거한다.
currentSqlSession.realClose();
currentSqlSession = null;
// 트랜잭션을 종료할 때 진짜 SqlSession 객체를 닫는다.
}
public SqlSession openSession() {
if (inTransaction) {
if (currentSqlSession == null) {
// 트랜잭션이 시작 중일 때는 수동 커밋 상태의 SqlSession을 만든다.
// 나중에 다시 쓸 수 있도록 보관해둔다.
currentSqlSession = new SqlSessionProxy(original.openSession());
return currentSqlSession;
}
// 기존에 만든 SqlSession을 리턴해준다.
// 왜? 같은 SqlSession을 리턴해줘야 여러 작업을 한 트랜잭션으로 묶을 수 있다.
return currentSqlSession;
}
// 트랜잭션이 시작 중이 아닐 때는 자동 커밋 상태의 SqlSession을 리턴한다.
// 따로 보관해두지 않는다.
return original.openSession(true);
}
이제 프로젝트를 삭제하다가 예외가 발생하면 commit을 하지 않고 rollback을 한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
명령> /project/delete
[프로젝트 삭제]
번호? 23
정말 삭제하시겠습니까?(y/N) y
프로젝트 삭제 중 오류 발생!
java.lang.Exception: 일부러 예외 발생!
--------------------------------------------------------------
명령어 실행 중 오류 발생: java.lang.NullPointerException
--------------------------------------------------------------
명령> at com.eomcs.pms.dao.mariadb.ProjectDaoImpl.delete(ProjectDaoImpl.java:43)
at com.eomcs.pms.handler.ProjectDeleteCommand.execute(ProjectDeleteCommand.java:37)
at com.eomcs.pms.filter.DefaultCommandFilter.doFilter(DefaultCommandFilter.java:24)
at com.eomcs.pms.filter.CommandFilterManager$Chain.doFilter(CommandFilterManager.java:55)
at com.eomcs.pms.filter.LogCommandFilter.doFilter(LogCommandFilter.java:24)
at com.eomcs.pms.filter.CommandFilterManager$Chain.doFilter(CommandFilterManager.java:55)
at com.eomcs.pms.App.service(App.java:121)
at com.eomcs.pms.App.main(App.java:69)
/project/detail
[프로젝트 상세보기]
번호? 23
프로젝트명: test100
내용: okok
기간: 2020-01-01 ~ 2020-02-02
관리자: hayeon
팀원: hayeon ccc bbb moni
작업:
------------------------------------
번호, 작업내용, 마감일, 작업자, 상태
10, task1, 2020-01-01, moni, 진행중
11, task, 2020-01-01, bbb, 진행중
4단계: 모든 DAO 클래스에서 자동 커밋을 수동 커밋으로 변경한다.
XxxDaoImpl 클래스 변경
openSession(true)코드를openSession()으로 변경한다.- 즉 트랜잭션 통제권을 DAO를 사용하는 측에 넘긴다.
ProjectAddCommand나ProjectUpdateCommand는 커밋을 할 필요가 없다.insert를 한 번만 호출하기 때문이다.findBy~는select이기 때문에 커밋이 필요 없다.
ProjectUpdateCommand 클래스를 변경한다.
- 프로젝트 정보를 변경할 때 팀원 정보를 변경하지 않는다.
프로젝트 팀원 정보를 변경한다면, 이것에 얽혀 있는
Task의 담당자까지 변경해야 하기 때문이다. 따라서 만약 멤버를 변경한다면 데이터 무결성 원칙에 위배된다. 이는 추후에 HTML로 넘어갈 때 변경할 것이다.
ProjectDaoImpl.update()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
@Override
public int update(Project project) throws Exception {
try (SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession()) {
int count = sqlSession.update("ProjectDao.update", project);
if (count == 0) {
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
}
