스택
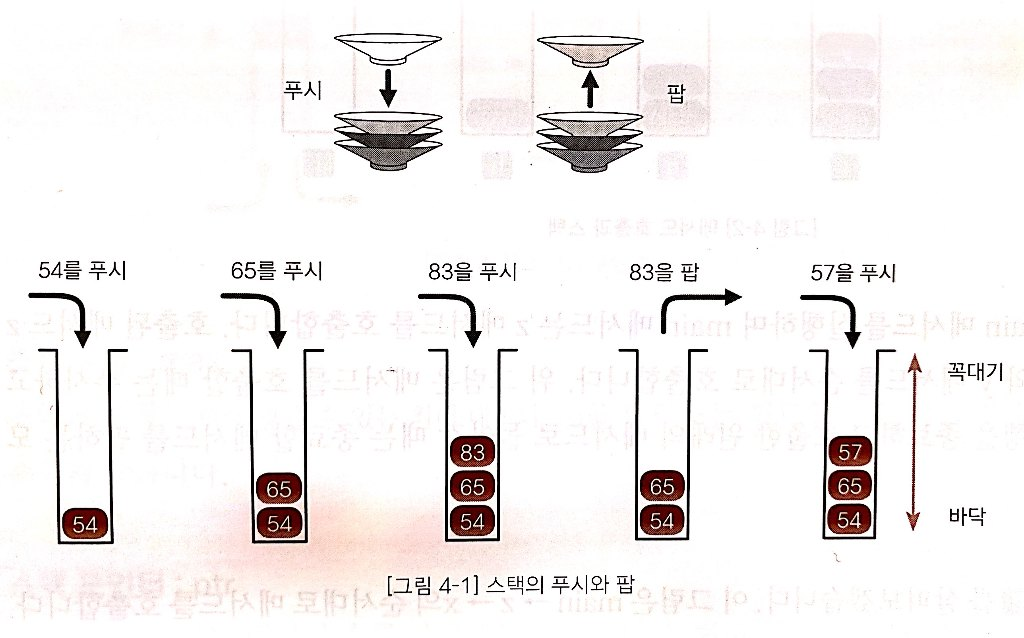
- 데이터를 일시적으로 저장하기 위한 자료구조로
- LIFO: 가장 나중에 넣은 데이터를 가장 먼저 꺼낸다.
- 푸시와 팝을 하는 위치를 top이라고 하고, 스택의 가장 아랫부분을 bottom이라고 한다.
실습4-1. IntStack
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
package algorithm.doit.ch04;
public class IntStack {
private int max; // 스택 용량
private int ptr; // 스택 포인터
private int[] stk; // 스택 본체
// 실행 시 예외: 스택이 비어 있음
public class EmptyIntStackException extends RuntimeException {
public EmptyIntStackException() {}
}
// 실행 시 예외: 스택이 가득
public class OverflowIntStackException extends RuntimeException {
public OverflowIntStackException() {
}
}
public IntStack(int capacity) {
ptr = 0;
max = capacity;
try {
stk = new int[max];
} catch (OutOfMemoryError e) {
max = 0;
}
}
public int push(int x) throws OverflowIntStackException {
if (ptr == max)
throw new OverflowIntStackException();
return stk[ptr++] = x;
}
public int pop() throws EmptyIntStackException {
if (ptr == 0)
throw new EmptyIntStackException();
return stk[--ptr];
}
public int peek() throws EmptyIntStackException {
if (ptr == 0)
throw new EmptyIntStackException();
return stk[ptr -1];
}
public int indexOf(int key) {
for (int i = ptr - 1; i <= 0; i--) {
if (stk[i] == key)
return i;
}
return -1;
}
// 스택에 대한 푸시와 팝 등 모든 작업은 스택 포인터를 바탕으로 이루어진다.
// 따라서 스택의 배열 요솟값을 변경할 필요가 없다.
// 모든 요소의 삭제는 스택 포인터 ptr 값을 0으로 하면된다.
public void clear() {
ptr = 0;
}
public int capacity() {
return max;
}
public int size() {
return ptr;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return ptr <= 0;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return ptr >= max;
}
// 스택 안의 모든 데이터를 바닥 -> 꼭대기 순서로 출력
public void dump() {
if (ptr <= 0) {
System.out.println("스택이 비어있습니다.");
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < ptr; i++)
System.out.println(stk[i]);
System.out.println();
}
}
}
실습 4-2. IntStackTester
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
public class IntStackTester {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
IntStack s = new IntStack(64);
while (true) {
System.out.println("현재 데이터 수: " + s.size() +" / " + s.capacity());
System.out.println("(1) 푸시 (2) 팝 (3) 피크 (4) 덤프 (0) 종료 ");
int menu = sc.nextInt();
if (menu == 0) return;
switch (menu) {
case 1:
System.out.print("데이터: ");
int x = sc.nextInt();
try {
s.push(x);
} catch (IntStack.OverflowIntStackException e) {
System.out.println("스택이 가득 찼습니다.");
}
break;
case 2:
try {
x = s.pop();
System.out.println("팝한 데이터는 " + x + "입니다.");
} catch (IntStack.EmptyIntStackException e) {
System.out.println("스택이 비어 있습니다.");
}
break;
case 3:
try {
x = s.peek();
System.out.println("피크한 데이터는 " + x + "입니다.");
} catch (IntStack.EmptyIntStackException e) {
System.out.println("스택이 비어 있습니다.");
}
break;
case 4:
s.dump();
break;
}
}
}
}
연습문제 Q1. IntStack의 모든 메서드를 사용하는 프로그램 작성
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
public class Q1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
IntStack s = new IntStack(64);
while (true) {
System.out.println("현재 데이터 수: " + s.size() +" / " + s.capacity());
System.out.println("(1) 푸시 (2) 팝 (3) 피크 (4) 덤프 (0) 종료 ");
System.out.println("(5) 클리어 (6) 용량 (7) 사이즈 (8) empty (9) full");
int menu = sc.nextInt();
if (menu == 0) return;
switch (menu) {
case 1:
System.out.print("데이터: ");
int x = sc.nextInt();
try {
s.push(x);
} catch (IntStack.OverflowIntStackException e) {
System.out.println("스택이 가득 찼습니다.");
}
break;
case 2:
try {
x = s.pop();
System.out.println("팝한 데이터는 " + x + "입니다.");
} catch (IntStack.EmptyIntStackException e) {
System.out.println("스택이 비어 있습니다.");
}
break;
case 3:
try {
x = s.peek();
System.out.println("피크한 데이터는 " + x + "입니다.");
} catch (IntStack.EmptyIntStackException e) {
System.out.println("스택이 비어 있습니다.");
}
break;
case 4:
s.dump();
break;
case 5:
s.clear();
break;
case 6:
System.out.println("스택의 용량은 " + s.capacity() + "입니다.");
break;
case 7:
System.out.println("스택의 사이즈는 " + s.size()+ "입니다.");
break;
case 8:
if (s.isEmpty())
System.out.println("네, 스택은 비어있습니다.");
System.out.println("아니오, 스택은 비어있지 않습니다.");
break;
case 9:
if (s.isFull())
System.out.println("네, 스택이 꽉 찼습니다.");
System.out.println("아니오, 스택이 꽉 차지 않았습니다.");
break;
}
}
}
}
연습문제 Q2. 임의의 객체형 데이터를 쌓을 수 있는 제네릭 클래스 Gstack<E>를 작성하세요.
IntStack을 만들 때와 달리 Gstack에서 중첩 클래스 EmptyGstackException, OverflowGstackException을 만들 때는 주의해야 했다. 처음에 IntStack에서 한 것과 똑같이 각각의 중첩 클래스를 static 없이 non-static중첩 클래스(inner class)로 선언하였다. 그러나 컴파일 에러가 발생하였다. 에러 내용은 “Gstack<E>.EmptyGstackException may not subclass java.lang.Throwable”이었다. 찾아보니 제네릭 클래스의 경우 Throwable 객체를 상속할 수 없다는 규칙이 있었다.
그렇다면 왜 EmptyGstackException은 제네릭 클래스도 아닌데 non-static 클래스일 경우 컴파일 에러가 발생하는 걸까? 그것은 중첩 클래스를 non-static으로 선언할 경우 바깥 클래스(Gstack)의 인스턴스에 종속되기 때문이다. 따라서 제네릭에도 영향을 받는다. 그러나 static으로 선언할 경우 중첩 클래스는 단지 바깥 클래스의 내부에 위치할 뿐, 바깥 클래스의 인스턴스에 독립적이다. 따라서 컴파일러 입장에서는 top-level-class 나 마찬가지이다. 따라서 Throwable의 하위 클래스인 RuntimeException을 상속받을 수 있다. 자바는 제네릭 컴파일 에러 내용은 Gstack은 제네릭 클래스이다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
public class Gstack <E> {
private int max; // 스택 용량
private int ptr; // 스택 포인터
private E[] stk; // 스택 본
public static class EmptyGstackException extends RuntimeException {
public EmptyGstackException() {
}
}
public static class OverflowGstackException extends RuntimeException {
public OverflowGstackException() {
}
}
public Gstack(int capacity) {
ptr = 0;
max = capacity;
try {
stk = (E[]) new Object[max];
} catch (OutOfMemoryError e) {
max = 0;
}
}
public E push(E x) throws OverflowGstackException {
if (ptr == max)
throw new OverflowGstackException();
return stk[ptr++] = x;
}
public E pop() throws EmptyGstackException {
if (ptr == 0)
throw new EmptyGstackException();
return stk[--ptr];
}
public E peek() throws EmptyGstackException {
if (ptr == 0)
throw new EmptyGstackException();
return stk[ptr -1];
}
public int indexOf(E key) {
for (int i = ptr - 1; i <= 0; i--) {
if (stk[i].equals(key))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
public void clear() {
ptr = 0;
}
public int capacity() {
return max;
}
public int size() {
return ptr;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return ptr <= 0;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return ptr >= max;
}
public void dump() {
if (ptr <= 0) {
System.out.println("스택이 비어있습니다.");
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < ptr; i++)
System.out.println(stk[i]);
System.out.println();
}
}
}
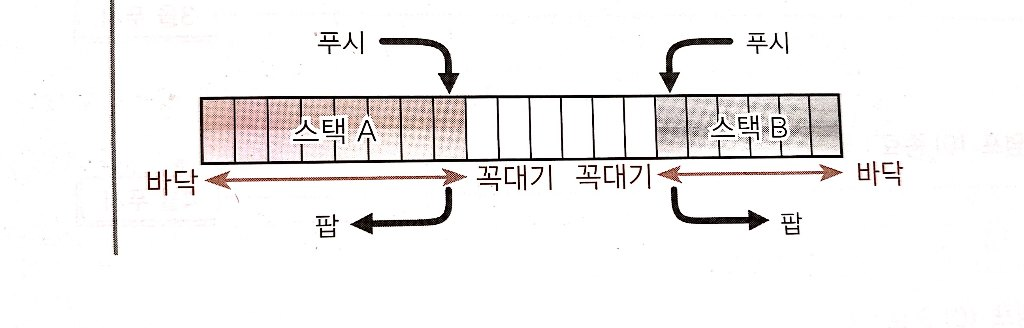
**연습문제 Q3. ** 하나의 배열을 공유하여 2개의 스택을 구현하는 int형 데이터용 스택 클래스를 만들기.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
public class Q3 {
private int max; // 스택 용량
private int ptrA; // 스택 포인터
private int ptrB;
private int[] stk; // 스택 본체
public enum WhichStack { stackA, stackB }
// 실행 시 예외: 스택이 비어 있음
public class EmptyIntStackException extends RuntimeException {
public EmptyIntStackException() {}
}
// 실행 시 예외: 스택이 가득
public class OverflowIntStackException extends RuntimeException {
public OverflowIntStackException() {
}
}
public Q3(int capacity) {
ptrA = 0;
ptrB = capacity - 1; // ptr은 인덱스
max = capacity;
try {
stk = new int[max];
} catch (OutOfMemoryError e) {
max = 0;
}
}
public int push(WhichStack stack, int x) throws OverflowIntStackException {
if (ptrA >= ptrB + 1) {
throw new OverflowIntStackException();
}
switch (stack) {
case stackA:
return stk[ptrA++] = x;
default:
return stk[ptrB--] = x;
}
}
public int pop(WhichStack stack) throws EmptyIntStackException {
switch (stack) {
case stackA:
if (ptrA <= 0)
throw new EmptyIntStackException();
return stk[--ptrA];
default:
if (ptrB >= max - 1)
throw new EmptyIntStackException();
return stk[++ptrB];
}
}
public int peek(WhichStack stack) throws EmptyIntStackException {
switch (stack) {
case stackA:
if (ptrA == 0)
throw new EmptyIntStackException();
return stk[ptrA - 1];
default:
if (ptrB == max - 1)
throw new EmptyIntStackException();
return stk[ptrB + 1];
}
}
public int indexOf(WhichStack stack, int key) {
switch(stack) {
case stackA:
for (int i = ptrA - 1; i <= 0; i--) {
if (stk[i] == key)
return i;
}
break;
default:
for (int i = ptrB + 1; i > max; i++) {
if (stk[i] == key)
return i;
}
break;
}
return -1;
}
public void clear(WhichStack stack) {
switch (stack) {
case stackA:
ptrA = 0;
break;
default:
ptrB = max;
}
}
public int capacity() {
return max;
}
public int size(WhichStack stack) {
switch (stack) {
case stackA:
return ptrA;
default:
return max - ptrB - 1;
}
}
public boolean isEmpty(WhichStack stack) {
switch (stack) {
case stackA:
return ptrA <= 0;
default:
return ptrB >= max - 1;
}
}
public boolean isFull() {
return ptrA >= ptrB + 1;
}
// 스택 안의 모든 데이터를 바닥 -> 꼭대기 순서로 출력
public void dump(WhichStack stack) {
switch (stack) {
case stackA:
if (ptrA <= 0)
System.out.println("스택이 비어있습니다.");
else {
for (int i = 0; i < ptrA; i++)
System.out.println(stk[i] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
break;
default:
if (ptrB >= max)
System.out.println("스택이 비어있습니다.");
else {
for (int i = max; i > ptrB; i--)
System.out.println(stk[i] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
break;
}
}
}
큐
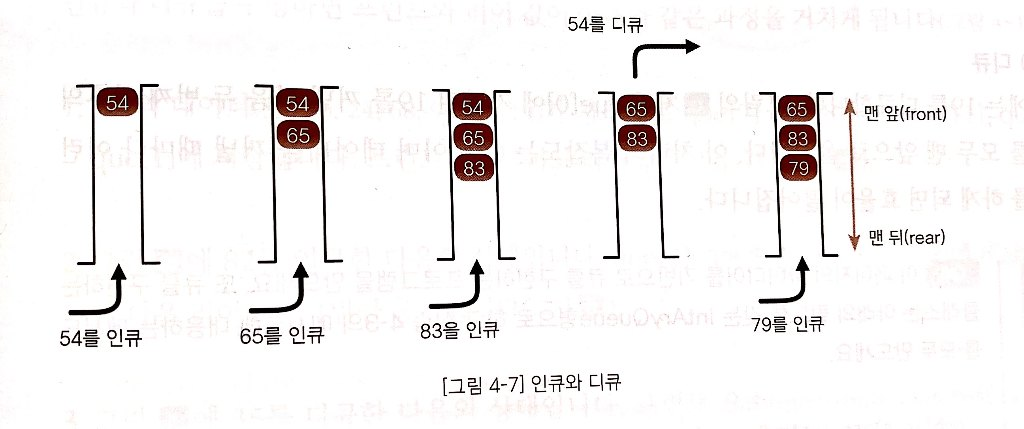
- 데이터를 일시적으로 쌓아 놓은 자료구조
- 가장 먼저 넣은 데이터를 가장 먼저 꺼내는 선입선출(FIFO; First In First Out)이다.
- 은행 창구에서 차례를 기다리는 대기열, 마트에서 계산을 기다리는 대기줄
- 데이터를 꺼내는 쪽을 front, 데이터를 넣는 쪽을 rear라고 한다.
연습문제 Q4. 큐를 구현하는 프로그램을 만드세요.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
public class IntAryQueue {
private int max;
private int num;
private int[] que;
public class EmptyIntAryQueueException extends RuntimeException {
public EmptyIntAryQueueException() {}
}
public class OverflowIntAryQueueException extends RuntimeException {
public OverflowIntAryQueueException() {}
}
public IntAryQueue (int capacity) {
max = capacity;
num = 0;
try {
que = new int[max];
} catch (OutOfMemoryError e) {
max = 0;
}
}
public int enque(int x) throws OverflowIntAryQueueException {
if (num >= max)
throw new OverflowAryQueueException();
que[num++] = x;
return x;
}
public int deque() throws EmptyIntAryQueueException {
if (num <= 0)
throw new EmptyIntAryQueueException();
int x = que[0];
for (int i = 0; i < num - 1; i++) {
que[i] = que[i-1];
}
num--;
return x;
}
public int indexOf(int x) {
for (int i = 0 ; i < num; i++) {
if (que[i] == x)
return i;
}
return -1;
}
public void clear() {
num = 0;
}
public int capacity() {
return max;
}
public int size() {
return num;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return num <= 0;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return num >= max;
}
public void dump() {
if (num <= 0)
System.out.println("큐가 비었습니다.");
else {
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++)
System.out.print(que[i] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
}
링 버퍼로 큐 만들기
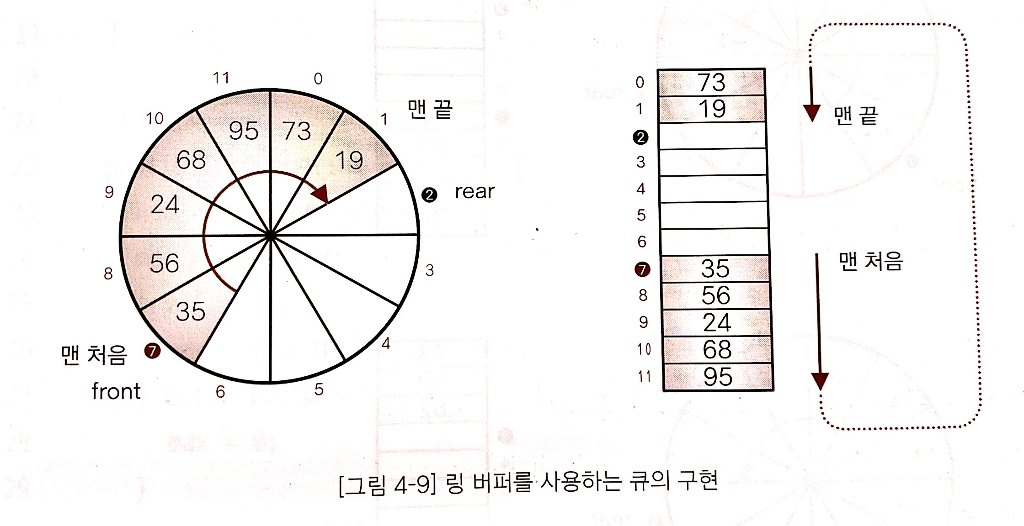
링 버퍼(ring buffer): 배열 요소를 앞쪽으로 옮기지 않는 큐 구현에 사용하는 자료구조
- front: 맨 처음 요소의 인덱스
rear: 맨 끝 요소의 하나 뒤의 인덱스(다음 요소를 인큐할 위치를 미리 지정)
- 프런트와 리어값을 업데이트하며 인큐와 디큐를 수행하면 요소 이동 문제를 해결할 수 있다.
- 처리의 복잡도는 O(1)이다.
- 연습문제 4에서 구현한 큐는 요소 이동을 수행하기 때문에 복잡도가 O(n)이다.
실습 4-1~3. IntQueue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
public class IntQueue {
private int max; // 큐의 용량
//첫 번째 요소 커서
//인큐하는 데이터 가운데 첫번째 요소 위치. 디큐할 위치를 미리 저장
private int front;
private int rear; // 마지막 요소 커서(다음 요소를 인큐할 위치를 미리 저장!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!)
// front와 rear의 값이 같은 경우 큐가 비어있는 지 가득 차 있는지 구별할 수 없는 상황을 피하기 위해서 이 변수가 필요ㅕ하다.
// 큐가 비어 있을 때 num==0(front==rear==0), 다 차있을때 num == max
private int num; // 현재 데이터 수
private int[] que; // 큐 본체
// 실행 시 예외: 큐가 비어 있음
public class EmptyIntQueueException extends RuntimeException {
public EmptyIntQueueException() {}
}
// 실행 시 예외: 큐가 가득 참
public class OverflowIntQueueException extends RuntimeException {
public OverflowIntQueueException() {}
}
// 생성자
public IntQueue(int capacity) {
num = front = rear = 0;
max = capacity;
try {
que = new int[max]; // 큐 본체용 배열을 생성
} catch (OutOfMemoryError e) { // 생성할 수 없음
max = 0;
}
}
public int enque(int x) throws OverflowIntQueueException {
if (num >= max)
throw new OverflowIntQueueException();
que[rear++] = x;
num++;
if (rear == max)
rear = 0;
return x;
}
public int deque() throws EmptyIntQueueException {
if (num <= 0)
throw new EmptyIntQueueException();
int x = que[front++];
num--;
if (front == max)
front = 0;
return x;
}
public int peek() throws EmptyIntQueueException {
if (num <= 0)
throw new EmptyIntQueueException();
return que[front];
}
public int indexOf(int x) {
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
int idx = (i + front) % max;
if (que[idx] == x)
return idx;
}
return -1;
}
// 모든 데이터를 삭제하는 메서드
// 인큐, 디큐는 num, front, rear 값을 바탕으로 0으로 바꾼다. 실제 큐의 배열 요솟값을 바꿀 필요가 없다.
public void clear() {
num = front = rear = 0;
}
public int capacity() {
return max;
}
public int size() {
return num;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return num <= 0;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return num >= max;
}
// 큐 안의 모든 데이터를 프런트 -> 리어 순으로 출력
public void dump() {
if (num < 0)
System.out.println("큐가 비어 있습니다.");
else {
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++)
System.out.print(que[(i + front) % max] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
}
실습 4-4. IntQueueTester
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
public class IntQueueTester {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
IntQueue s = new IntQueue(64);
while (true) {
System.out.println("현재 데이터 수: " + s.size() + " /" + s.capacity());
System.out.print("(1) 인큐 (2) 디큐 (3) 피크 (4) 덤프 (0) 종료: ");
int menu = sc.nextInt();
if (menu == 0) break;
int x;
switch (menu) {
case 1:
System.out.print("데이터: ");
x = sc.nextInt();
try {
s.enque(x);
} catch (IntQueue.OverflowIntQueueException e) {
System.out.println("큐가 가득 찼습니다.");
}
break;
case 2:
try {
x = s.deque();
System.out.println("디큐한 데이터는 " + x + "입니다.");
} catch (IntQueue.EmptyIntQueueException e) {
System.out.println("큐가 비어있습니다.");
}
break;
case 3:
try {
x = s.peek();
System.out.println("피크한 데이터는 " + x + "입니다.");
} catch (IntQueue.EmptyIntQueueException e) {
System.out.println("큐가 비어있습니다.");
}
break;
case 4:
s.dump();
break;
}
}
}
}
연습문제 Q5 클래스 IntQueue에 임의의 데이터를 검색하는 메서드를 추가
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
public int search(int x) {
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
if (que[(front + i) % max] == x)
return i + 1;
}
return 0;
}
연습문제 Q6. 임의의 객체형 데이터를 쌓아 놓을 수 있는 제네릭 큐 클래스 Gqueue<E>를 작성한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
public class Gqueue<E> {
private int max;
private int num;
private int front;
private int rear;
private E[] que;
public static class EmptyGqueueException extends RuntimeException {
public EmptyGqueueException() {}
}
// 실행 시 예외: 큐가 가득 참
public static class OverflowGqueueException extends RuntimeException {
public OverflowGqueueException() {}
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public Gqueue(int capacity) {
int max = capacity;
try {
que = (E[]) new Object[max];
} catch (OutOfMemoryError e) {
max = 0;
}
}
public E enque(E x) throws OverflowGqueueException {
if (num >= max)
throw new OverflowGqueueException();
que[rear++] = x;
num++;
if (rear == max)
rear = 0;
return x;
}
public E deque() throws EmptyGqueueException {
if (num < 0)
throw new EmptyGqueueException();
E x = que[front++];
num--;
if (front == max)
front = 0;
return x;
}
public E peek() throws EmptyGqueueException {
if (num < 0)
throw new EmptyGqueueException();
return que[front];
}
public int indexOf(E x) {
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
int idx = (i + front) % max;
if (que[idx] == x)
return idx;
}
return -1;
}
public void clear() {
num = front = rear = 0;
}
public int capacity() {
return max;
}
public int size() {
return num;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return num >= max;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return num <= 0;
}
public void dump() {
if (num < 0)
System.out.println("큐가 비어있습니다.");
else {
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++)
System.out.println(que[(i + front) % max] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
}
연습문제 Q7. 양방향 대기열을 구현하는 클래스 IntDeque 만들기
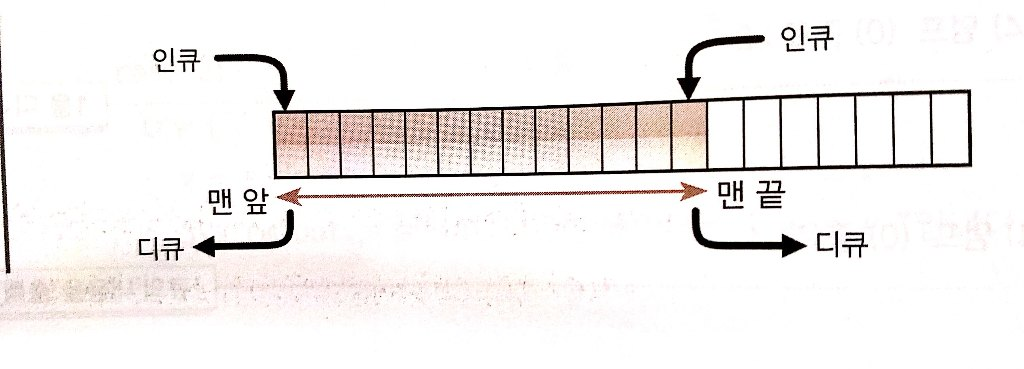
- 시작과 끝 지점에서 데이터를 인큐하거나 디큐하는 자료구조
- 양방향 대기열(deque/double ended queue)인 덱(deck)구현
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
public class IntDeque {
private int max;
private int num;
private int front;
private int rear;
private int[] que;
public IntDeque(int capacity) {
max = capacity;
que = new int[max];
}
public class OverflowIntDequeueException extends RuntimeException {
public OverflowIntDequeueException() {}
}
public class EmptyIntDequeueException extends RuntimeException {
public EmptyIntDequeueException() {}
}
public int enqueFront(int x) throws OverflowIntDequeueException {
if (num >= max)
throw new OverflowIntDequeueException();
if (--front < 0)
front = max - 1;
que[front] = x;
num++;
return x;
}
public int enqueRear(int x) throws OverflowIntDequeueException {
if (num >= max)
throw new OverflowIntDequeueException();
que[rear++] = x;
num++;
if (rear == max)
rear = 0;
return x;
}
public int dequeFront() throws EmptyIntDequeueException {
if (num <= 0)
throw new EmptyIntDequeueException();
int x = que[++front];
num--;
if (front == max)
front = 0;
return x;
}
public int dequeRear() throws EmptyIntDequeueException {
if (num <= 0)
throw new EmptyIntDequeueException();
num--;
if (--rear < 0)
rear = max - 1;
return que[rear];
}
public int peekFront() throws EmptyIntDequeueException {
if (num <= 0)
throw new EmptyIntDequeueException();
return que[front];
}
public int peekRear() throws EmptyIntDequeueException {
if (num <= 0)
throw new EmptyIntDequeueException();
return que[rear == 0 ? max - 1 : rear - 1];
}
public int indexOf(int x) {
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
int idx = (front + i) % max;
if (que[idx] == x)
return idx;
}
return -1;
}
public int search(int x) {
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
if (que[(front + i) % max] == x)
return i;
}
return -1;
}
public void clear() {
num = front = rear = 0;
}
public int capacity() {
return max;
}
public int size() {
return num;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return num <= 0;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return num >= max;
}
public void dump() {
if (num <= 0)
System.out.println("deck이 비었습니다.");
else {
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++)
System.out.print(que[(i + front) % max] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
}
링 버퍼의 활용

- 링 버퍼는 오래된 데이터를 버리는 용도로 사용할 수 있다.
- 다음 예제는 정수 입력(인큐)는 무한히 할 수 있지만 배열에 저장되는 데이터는 가장 최근에 입력한 10개의 데이터만 링 버퍼에 남아 있다.
실습 4C-1 LastNElements
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
public class LastNElements {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
final int N = 10;
int[] a = new int[N];
int cnt = 0;
int retry;
System.out.println("정수를 입력하세요.");
do {
System.out.printf("%d번째 정수: ", cnt + 1);
a[cnt++ % N] = sc.nextInt();
System.out.print("계속 할까요? (예.1/아니오.0): ");
retry = sc.nextInt();
} while (retry == 1);
int i = cnt - N;
if (i < 0) i = 0;
for (; i < cnt; i++)
System.out.printf("%2d번째의 정수=%d\n", i+1, a[i%N]);
}
}
