파이썬으로 그래프를 표현하는 방법
파이썬에서 제공하는 딕셔너리와 리스트 자료 구조를 활용해서 그래프를 표현할 수 있음
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
graph = dict()
graph['A'] = ['B', 'C']
graph['B'] = ['A', 'D']
graph['C'] = ['A', 'G', 'H', 'I']
graph['D'] = ['B', 'E', 'F']
graph['E'] = ['D']
graph['F'] = ['D']
graph['G'] = ['C']
graph['H'] = ['C']
graph['I'] = ['C', 'J']
graph['J'] = ['I']
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
{'A': ['B', 'C'],
'B': ['A', 'D'],
'C': ['A', 'G', 'H', 'I'],
'D': ['B', 'E', 'F'],
'E': ['D'],
'F': ['D'],
'G': ['C'],
'H': ['C'],
'I': ['C', 'J'],
'J': ['I']}
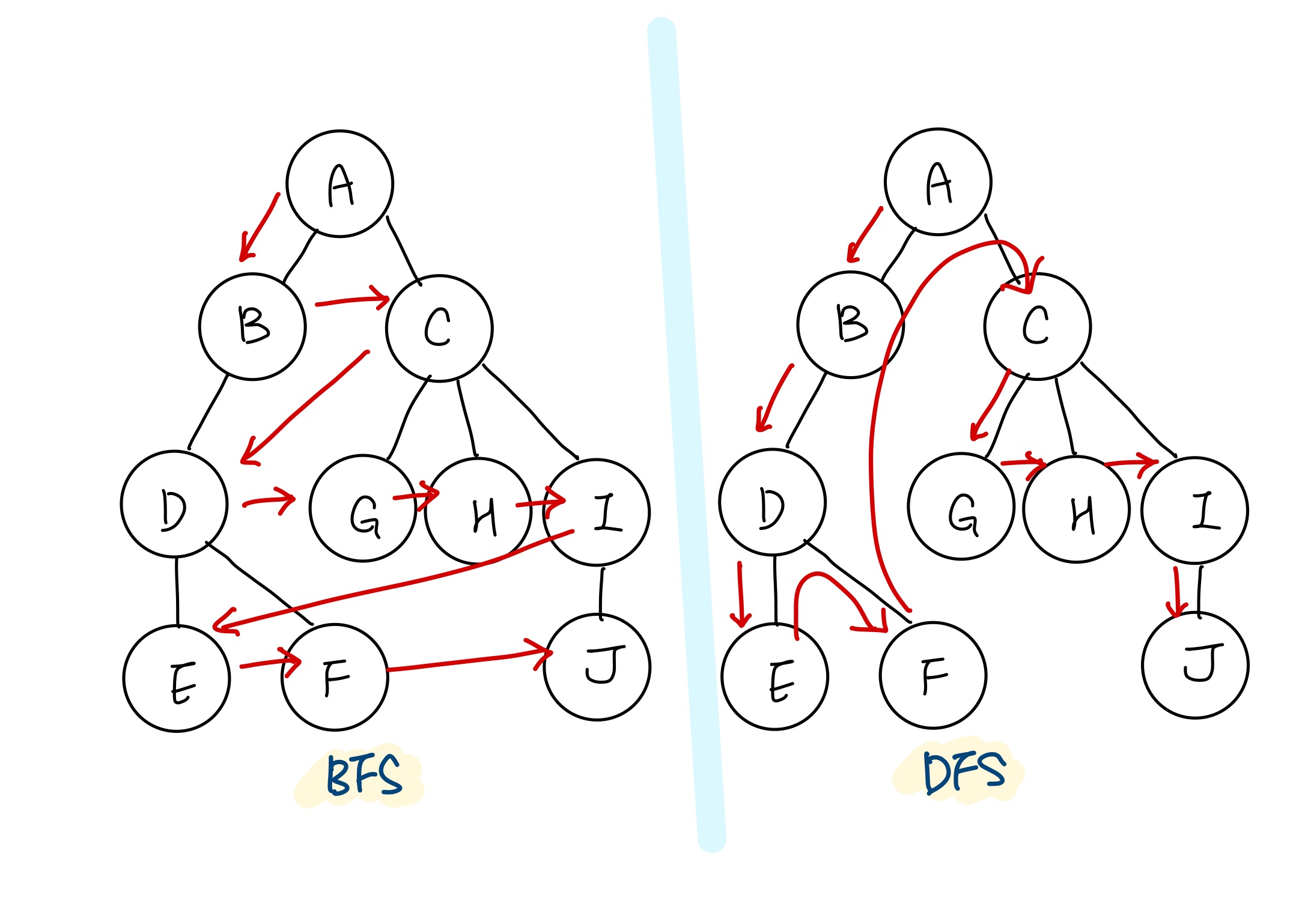
BFS 알고리즘 구현
자료구조 큐를 이용함: need_visit 큐와 visited 큐 두 개의 큐를 생성
- 큐의 구현은 간단히 파이썬 리스트를 활용
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
def bfs(graph, start_node):
visited, need_visit = list(), list()
need_visit.append(start_node)
while need_visit:
node = need_visit.pop(0)
if node not in visited:
visited.append(node)
need_visit.extend(graph[node])
return visited
DFS 알고리즘 구현
- 자료구조 스택과 큐를 활용함
- need_visit 스택과 visited 큐, 두 개의 자료구조를 생성
BFS 자료구조는 두 개의 큐를 활용하는데 반해, DFS는 스택과 큐를 활용한다.
- 큐와 스택 구현은 별도 라이브러리를 통해 할 수도 있지만, 간단히 파이썬 리스트를 활용할 수도 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
def dfs(graph, start_node):
visited, need_visit = list(), list()
need_visit.append(start_node)
while need_visit:
node = need_visit.pop()
if node not in visited:
visited.append(node)
need_visit.extend(graph[node])
return visited
1
2
print(dfs(graph, 'A'))
# ['A', 'C', 'I', 'J', 'H', 'G', 'B', 'D', 'F', 'E']
시간 복잡도
일반적인 BFS, DFS 시간 복잡도
- 노드 수: V
- 간선 수: E
- 위 코드에서 while need_visit은 V + E번 수행함
- 시간 복잡도: O(V+ E)
